Collection:
A group of individual objects called
as collection.
Why do we need collections in java?
Array
are not in dynamic nature. Once array size is defined we cannot modify the size
and add the elements. A new array must be created with bigger sized and all the
elements need to be copied to the new array.
Collection are used in situation where data is dynamic. Collection
have default methods for search, sort…etc. so programmer no need to write functions.
Overview:
interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>{
}
interface List<E> extends Collection<E>{
//Only care about position of the
object
//Elements can be added with specifying
the index
//If position is not specified element
will be added at the end of the list.
}
interface Set<E> extends Collections<E>{
//Unique
things only - No duplicates allowed
//if obj.equals(obj2)
than only one object will be available
}
interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>{
//Arranged
in a order of processing
}
Interface Map<K,v>{
//Contains
key value pairs
//things
with unique keys.
}
What are the methods declared in Collection interface
interface Collection<E> extends Iterabale<E>{
boolean add (E e);
boolean
remove (Object o);
int
size();
boolean isEmpty();
void
clear();
boolean contains(Object
o);
boolean
containsAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean
addAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean
retainAll(Collection c)
Iterator<E>
iterator();
}
Explain about List interface
Interface List<E> extends Collection<E>{
boolean addAll(int
position , Collection c)
E get(int
index)
E set(int
index, Object E)
Void add(int
position, Object E)
E
remove(int index)
Int indexOf(Object
O)
Int lastIndexOf(Object
o)
}
Class ArrayList { /*
implements List<E>, RandomAccess*/
//Implements RandomAccess, a
market interface , means it supports faster fetching
//insertion and deletion is slower
comparing to LinkedList
}
Class vector{/* implements List<E>, Random Access
*/
//Implements Random Access- a
market interface, means its supports faster fetching
//Thread Safe – Synchronised
}
Class LinkedList{ /* Implements List<E>, Queue */
//Elements are doubly linked list
– means forward and backwards – to one another
// Ideal choice to implement stack
or queue
//Fast insertion and deletion
//Implements Queue interface so
supports methods of pop, poll, remove
}
Interface
Set<E> extends Collection<E>{
//unique things only
//if obj1.equals(obj2) then only one object will be available
in set
}
//maintains
elements in sorted order
Interface
SortedSet<E> extends collectin<E>{
SortedSet<E> subset(E fromElement, E toElement)
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement)
SortedSet<E> headset(E toElement)
E first()
E last()
}
Interface
NavigableSet<E> extends SortedSet<E>{
E lower(E)
E floor(E)
E higher(E)
E ceiling(E)
E pollFirst()
E pollLast()
}
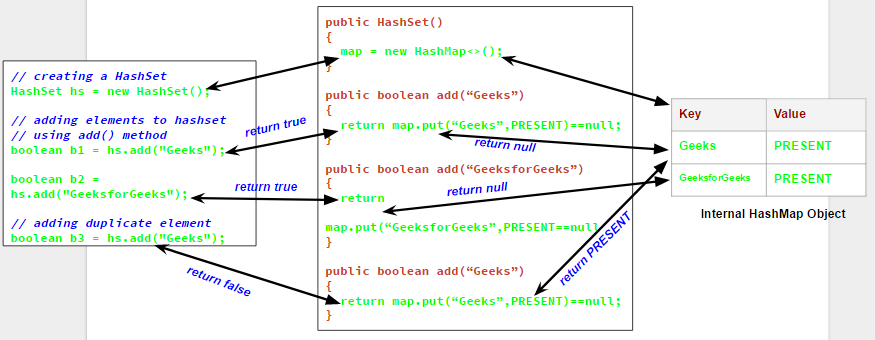
Class HashSet
{ /* implemnts set
*/
//unorderd, unsorted – iteraterates in
random order
//uses hashCode
}
Class LinkedHashSet
{ /* Implemnts Set
*/
//order – iterates in insertion order
//unsorted
//uses hashCode
}
Class TreeSet{
/* implements
navigableSet */
//sorted –
natural order
//implements
navigableset
}
Set/Hashset implementation: